- By JE Lifestyle Desk
- Fri, 05 Jan 2024 12:02 PM (IST)
- Source:JND
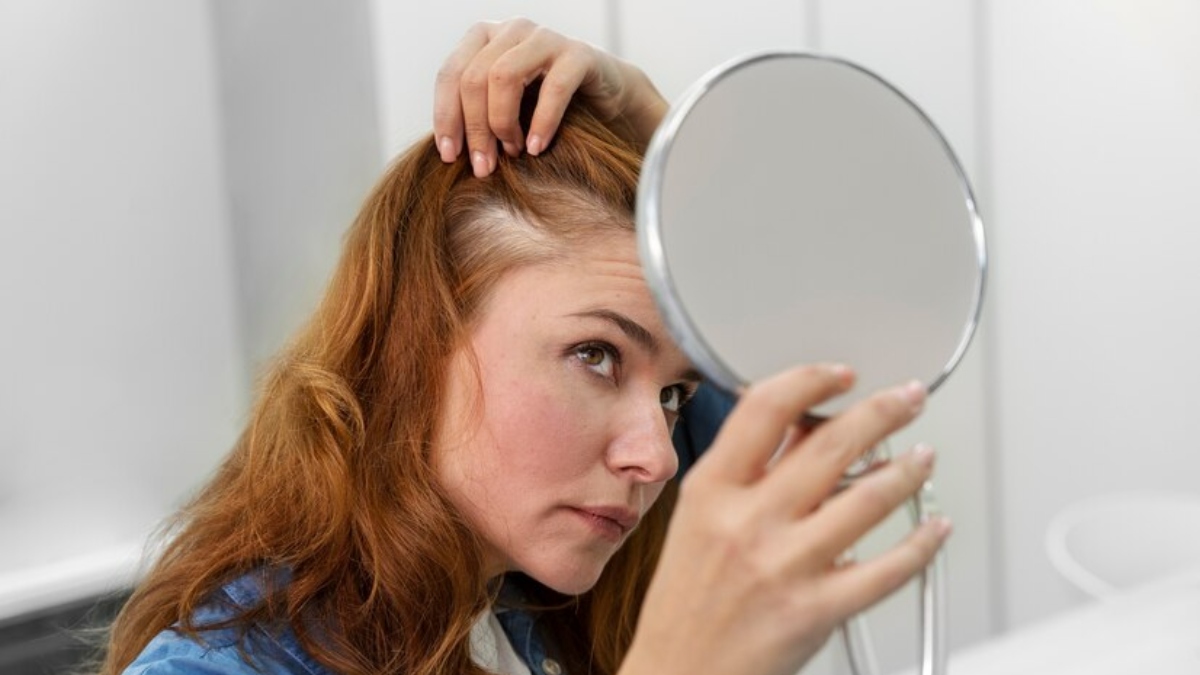
Hair thinning or hair loss can be caused by many different factors, including both controllable and uncontrollable circumstances. According to NHS(UK) statistics, around 50% of women over the age of 65 experience hair loss or hair thinning, and two-thirds of all men are affected. Although it’s a common issue – and usually nothing to worry about – thinning hair can be a difficult and upsetting process emotionally, impacting both our confidence and identity.
Rob Smith, Senior Principal Hair Care Scientist, Dyson gives a breakdown of the causes of hair thinning and effective ways to combat it.
Causes of hair loss
Thinning hair can occur for many different reasons. Age and stage of life can affect our health hugely and cause a change in the condition of our scalp. These include:
Pregnancy: During the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, the number of hairs in the active growth phase, known as anagen, increases. After the birth, hormonal changes can lead to follicles moving to the catagen or telogen states, resulting in post-pregnancy hair shedding.
Emotional stress: A sustained level of emotional stress after a serious life event, such as bereavement, can cause hair follicles to shift from the growing phase to the resting phase. After two to three months, this can often become more noticeable, even if it is temporary, with more hair thinning and fall out.
Getting older: Many people experience hair thinning during the ageing process. The rate of hair growth slows as your body ages, and each hair strand becomes smaller with less pigmentation – which is why people begin to develop grey hair.
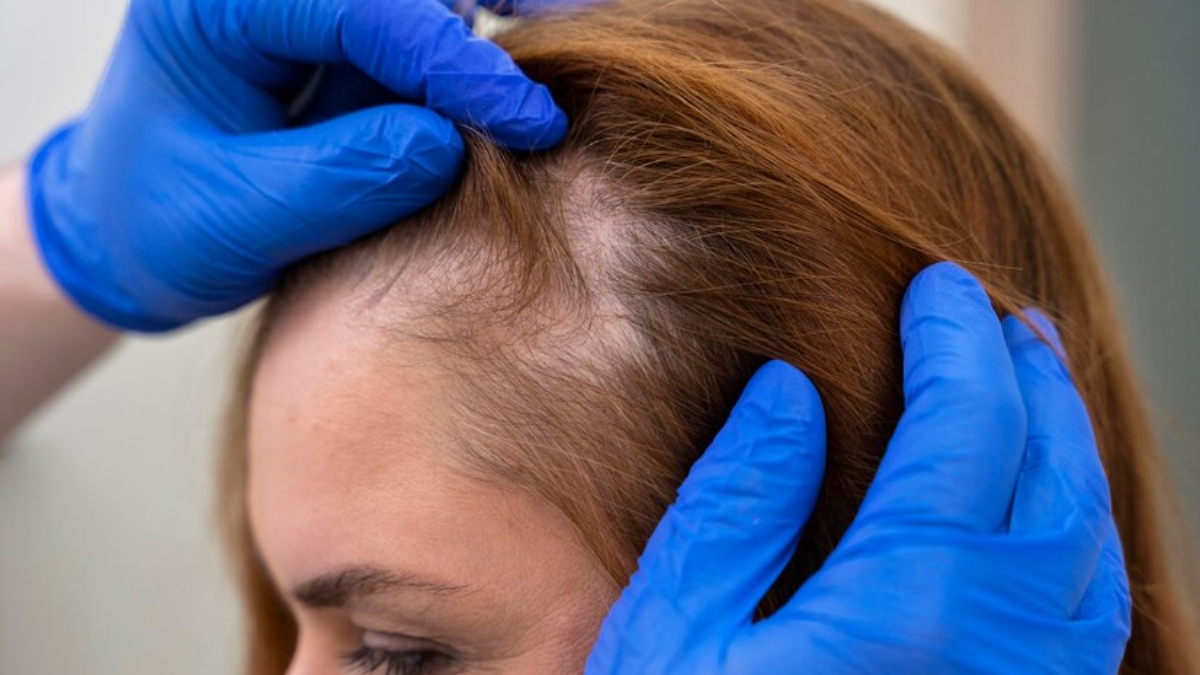
Illness: Thinning hair and hair loss can happen during illness. One such effect is an autoimmune condition called alopecia areata, a disease that develops when the body’s immune system attacks the hair follicles as part of its defence system, causing hair loss. This can happen anywhere on the body. Thinning hair and hair loss can occur during treatment for illness too. The main example includes cancer treatment, specifically during chemotherapy.
Hereditary hair loss: One established reason for hair loss is genetics, where hair loss isn’t the result of a disease, but a natural combination of hereditary genes, hormone levels, and the aging process.
If your hair continues to thin, there are a range of options to consider that can help hair appear thicker and fuller (Image:freepik)
Hormonal effects: The hair cycle and hair follicle structure are highly affected by various hormones. These include androgens such as testosterone, sex' hormones such as estradiol, thyroid hormones such as thyroxin and cortisol which is released by the adrenal glands as a stress response.
How to reduce or treat thinning hair?
Losing hair can be a difficult experience. Hair loss and thinning can stem from many different reasons, often exacerbated by lifestyle factors including high stress levels, an unbalanced diet, iron deficiency and sudden weight loss. But there are some things you can do. To maintain healthy, steady and effective hair growth, it’s important to prevent hair thinning from an early age.
Things you can do to promote hair growth include:
-Eating a healthy and balanced diet.
-Staying active to reduce stress and stimulate endorphins.
-Embracing relaxation techniques such as meditation and massage.
-Improving the balance of your work and personal life.
-If you are suffering from dietary or health deficiencies then the use of supplements can have a benefit on hair growth, but not all do so. In-fact in some cases consuming too much Vitamin E or Selenium can have the effect of actually increasing hair loss
If you’re interested in which shampoo or hair thinning treatment to use, the first step is trying to identify the source of the problem, to establish why your hair is shedding or falling out.

Hair thinning can be a difficult process to go through, but it is a natural part of life (Image:Freepik)
Can hair grow back after thinning or baldness?
In many cases, hair thinning can be resolved or improved by a variety of techniques. However, if the hair follicle has stopped producing any new hair strands over a long period of time, new hair is unlikely to grow there especially if the underlying causes remain.

