- By Anshika Verma
- Thu, 07 Aug 2025 11:01 PM (IST)
- Source:JND
Indian Army Rank Structure and Insignia: The Indian Army is the biggest military force in the world. It follows a well-defined structure of ranks. Every Army Ranks in India carry its own set of roles, responsibilities, powers and authority. These Indian Army Ranks are not just titles or positions, it reflect their experiences, command and a soldier’s place within the Indian Army from their responsibilities to execution. In this detailed article, we have discussed the Indian Army rank structure from the lower level to the highest level. Field Marshal is considered as the highest Army Ranks in India.
The insignia of the Indian Army, those striking symbols worn on uniforms aren’t just for decorations; these are the badges of honour, earned by these individuals through sweat, skill, and sacrifice. Indian Army Rank Structure is divided into three main categories- Commissioned Officers, Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs) and Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs).
Top 3 Pillars of the Indian Army:
The Indian Army is divided into three distinct groups. These three different groups are as follows:
1. Commissioned Officers (COs): The Commissioned Officers (COs) are popular military officers who hold their rank through a formal commission. These are the strategic commanders who lead with a powerful vision as well as authority.
2. Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs): Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs) are the senior non-commissioned officers who bridge the gap between the commissioned officers and enlisted soldiers. These soldiers use their experience and leadership in executing operations.
3. Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) and Soldiers: The officers are the foundation of the force, embodying grit and execution. Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) are the senior soldiers who hold the positions of authority to execute decisions within the military sector
Each category shows a progression of soldiers ranks, responsibilities, roles, and insignia, reflecting their journey.
Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) and Soldiers:
1. Sepoy (or Sowar in Cavalry/Armoured Units) Role: These are the enter-level officers, they are considered as the lifeblood of the Army. These soldiers guard borders, wield rifles, and charge into combat, they are often involved first to face danger and the last to stand there fighting for the country.
Insignia of Sepoy: No insignia adorns their shoulders, these soldiers have a plain badge, which symbolises its kind yet heroic beginning.
2. Lance Naik Role: Basically they are considered as the steps above from Sepoy, Lance Naiks supervise and handle a small team of 5-10 soldiers from ensuring discipline, plan execution to task completion. These soldiers are the first path of the leadership, they guide Sepoys with their experience and keen observation.
Insignia of Lance Naik: These officers hold a single upward-pointing chevron on their right sleeve that shows a modest symbol of emerging powers and leadership.
3. Naik Role: Naik soldiers handl sections of a total of 10-12 soldiers, checking their training, equipment training, and operational readiness. These soldiers translate the planning into achievable actionable steps, keeping units combat-ready.
Insignia of Naik: These soldiers have two chevrons, stacked proudly on their uniform, signaling their growing roles and responsibilities.These officers share a skill honed through their experience.
4. Havildar Role: These officers are the senior-most NCO, Havildars handle a team of 20-30 soldiers or take on specialised roles like Company Quarter Master Havildar (CQMH) training and execution. They usually train recruits, maintain morale and discipline, and make sure that there is operational efficiency.
Insignia: These soldiers have three chevrons form a bold triangle on their uniforms, which shows a testament to their seasoned leadership and strict leadership.
Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs): The Pillars of Experience
5. Naib Subedar (or Naib Risaldar in Cavalry)Role: These are the entry-level Junior Commissioned Officers, Naib Subedars handle platoons or assist in administrative operations. These officers mentor soldiers, ensure there is discipline, and ensure welfare, Naib Subedar is a role that requires both authority and empathy.
Insignia: These soldiers have one golden star with a single stripe on their uniforma subtle emblem or symbol of their new status.
6. Subedar (or Risaldar in Cavalry)Role: Subedars officers command larger units of people or mentor their training programs,it includes years of experience. These are considered as the trusted advisors to officers, who share their insights from the ground reality to refine strategies.
Insignia: These soldiers have two golden stars with a stripe on their uniform that shows a shining duo of leadership and their impressive legacy.
7. Subedar Major (or Risaldar Major in Cavalry) Role: The soldiers are considered as the highest Junior Commissioned Officers (JCOs) rank, Subedar Majors advise battalion commanders on how to improve discipline, welfare, and operations for hundreds of the soldiers. These soldiers are the embodiment of experience and faith.
Insignia: These soldiers have a golden National Emblem with a stripe on their uniform, that shows a prestigious symbol of their roles and responsibilities.
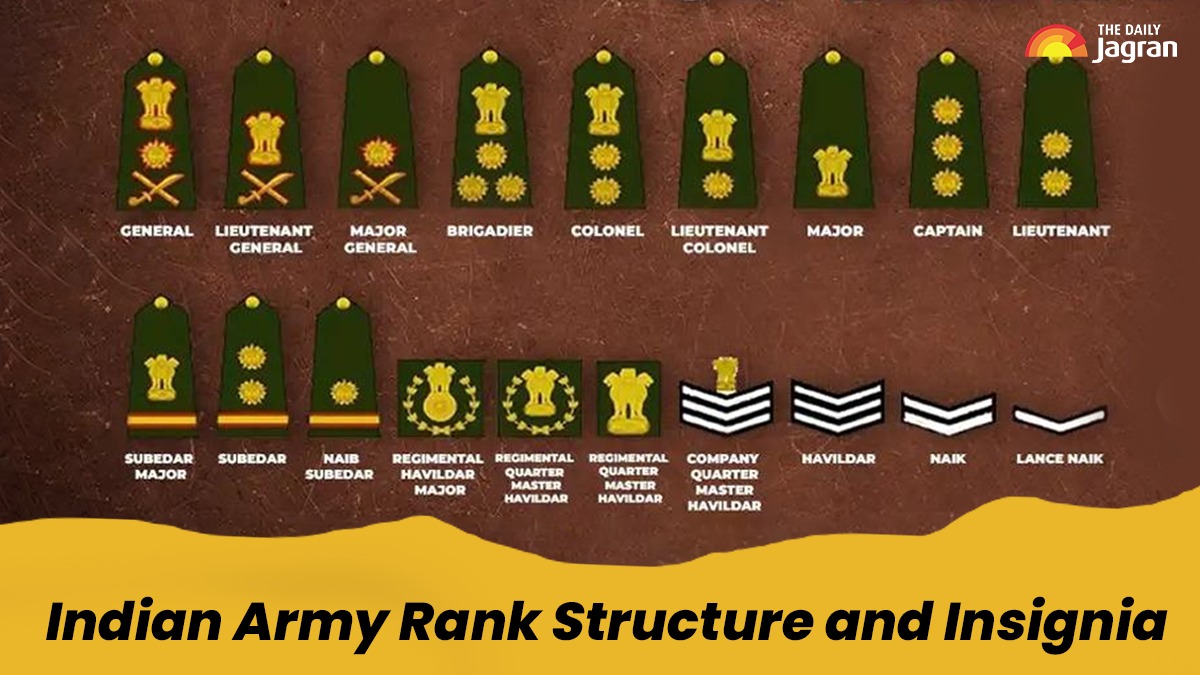
Commissioned Officers (COs):
8. Lieutenant : This is the beginning of the point for officers, Lieutenants lead platoons of a total of 30-40 soldiers, learning command and combat firsthand.
Insignia: These soldiers have two golden stars in a line—a bright startto a commanding career.
9. Captain: These captains handle 100-120 soldiers, from managing their training, logistics, and battlefield operations.
Insignia: They have three golden stars in a line on their uniform, which shows a trio that shows authority.
10. Major: These majors serve as second-in-command of soldiers (300-600 soldiers) and are popular for leading specialised units.
Insignia: They have one golden National Emblem which shows a bold mark of rising ability and performance.
11. Lieutenant Colonel: Lt. Colonels command battalions are those soldiers who oversee strategy and execution for hundreds of troops.
Insignia: They have a national Emblem with one star on their uniform with a fusion of prestige and power.
12. Colonel: Colonels are the officers who lead regiments or serve in staff roles, shaping operations and conducting training.
Insignia: These soldiers have a national Emblem with two stars which shows a commanding duo of authority.
13. Brigadier: Brigadiers are those commanders that handle (3,000-5,000 soldiers) with their experiences and strategy execution.
Insignia: These soldiers have a National Emblem with three stars on their official website.
14. Major General: Major Generals are those soldiers who oversee the divisions (10,000-15,000 soldiers).
Insignia: They have a crossed sword and baton with one star on their uniform.
15. Lieutenant General: Lt. Generals are the army commanders who oversee (30,000-50,000 soldiers).
Insignia: These soldiers have crossed swords and batons with the National Emblem on the uniform.
16. General: The Chief of Army Staff, a General, is popular for leading the entire Indian Army.
Insignia: These have a crossed sword and baton with one star and National Emblem.

