- By Chetna Shree
- Sat, 08 Nov 2025 10:33 PM (IST)
- Source:JND
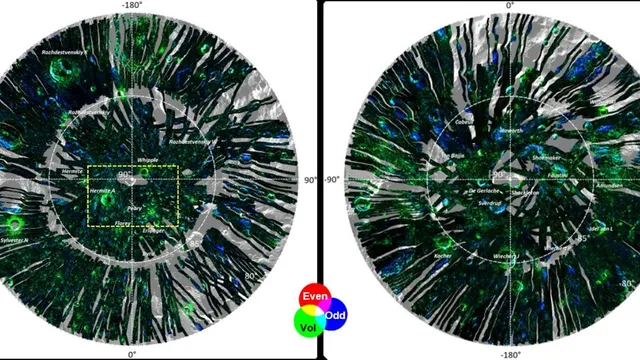
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has collected advanced data from its Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter and released it to boost a deeper understanding of the Moon’s polar regions. The orbiter’s Dual Frequency Synthetic Aperture Radar (DFSAR) offers clear, detailed pictures of the Moon’s polar regions, which can help scientists learn more about ice and the surface there.
In a post on X (formerly Twitter), ISRO wrote, “ISRO has come up with advanced data products from the Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter for a deeper understanding of the lunar polar regions. These include important parameters describing physical and dielectric properties of the Moon’s surface. This is India’s major value addition towards future global exploration of the Moon.”
ISRO has come up with advanced data products from the Chandrayaan-2 lunar orbiter for deeper understanding of the lunar polar regions. These include important parameters describing physical and dielectric properties of the Moon’s surface. This is India’s major value addition… pic.twitter.com/5w2eQ4OVky
— ISRO (@isro) November 8, 2025
According to ISRO, the Chandrayan-2 orbiter has been circling the Moon since 2019 and has been sending high-quality data.
Scientists at ISRO’s Space Applications Centre (SAC) in Ahmedabad have used Chandrayaan-2 data to create the first fully polarimetric L-band radar map of the Moon with a high resolution of 25 meters per pixel, Jagran.com reported.
The radar, one of the most advanced instruments ever built, sends and receives signals in both vertical and horizontal directions.
Using this data, the scientists at SAC in Ahmedabad have gained new insights into the Moon’s polar regions, including the possible presence of water ice and the density of the lunar surface. The scientists also developed specialised algorithms and data processing systems to analyse the full-polarimetric radar data.
(With PTI Inputs)