- By Kamal Kumar
- Thu, 19 Oct 2023 11:00 AM (IST)
- Source:JND
LEO: The Ganaganyaan -ISRO's endeavour prime and a dream shared by a billion Indians- is all set to be launched in 2025. Prime Minister Modi chaired a high-level meeting on October 16 to review the progress of Gaganyaan -India's first manned space mission- and defined the objectives of the future course of the country's ambitious plans in space.
Gaganyaan: The ace up ISRO's sleeve
Ganganyaan's mission aims to demonstrate ISRO's prowess in human spaceflight, with the ambitious goal of launching a human crew into a 400 km orbit and ensuring their safe return to Earth. With a resolute objective, the mission seeks to launch a human crew into a 400 km orbit, showcasing the technological prowess of ISRO by ensuring their safe return to Earth. With an investment of approximately Rs 9023 crore, this mission highlights India's dedication to advancing space exploration. The GSLV Mk III, now LVM-3, serves as the launch vehicle, revamped to meet stringent safety standards for human space travel.
This Collaborative effort will unite diverse entities, including the Indian Armed Forces, Defence Research Development Organization, academic institutions, and industry partners, fostering an inclusive approach. Training astronauts in Russia enhance their preparedness for weightlessness. Ultimately, the Gaganyaan Mission aspires not only to affirm India's human space capabilities but also to ignite scientific aspirations, encouraging pursuits in Science and Technology across the nation.
However, a question might persist why we have chosen the orbit of 400 kilometers? Why this periphery around the Earth is considered a part of space?
The answer is the LEO or Low Earth Orbit.
What is Low Earth Orbit?
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is a region of space extending approximately 160 to 2,000 kilometres above Earth's surface. This orbital zone is crucial for various satellite applications, including communication, Earth observation, and scientific research. Satellites in LEO have shorter orbital periods, facilitating more frequent revisits to specific areas.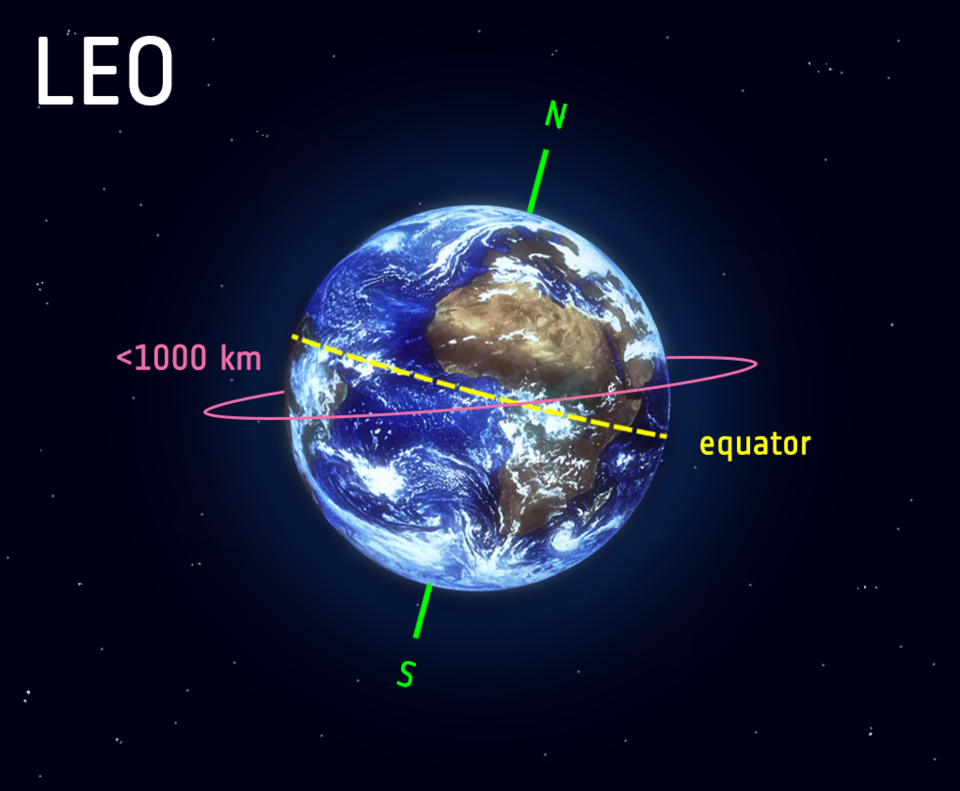
(Low Earth Orbit illustration by European Space Agency)
It's also the preferred location for crewed space missions and space stations due to lower radiation exposure. However, LEO is susceptible to atmospheric drag, requiring periodic adjustments. As a dynamic and accessible space domain, LEO plays a pivotal role in advancing space exploration, satellite technology, and understanding Earth's environment.
Why LEO is considered as a part of Space?
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is considered a part of space because it is a region beyond Earth's atmosphere where gravitational forces are still significant but allow for the stable orbital motion of objects. LEO typically extends from about 160 to 2,000 kilometres above Earth's surface. In this orbital zone, the influence of Earth's atmosphere is minimal compared to the vastness of outer space. Satellites and other objects in LEO experience microgravity conditions, allowing them to orbit the Earth without succumbing to atmospheric drag. LEO is a critical space domain for various applications, including satellite communication, Earth observation, scientific research, and human spaceflight endeavours.

