- By Iram Hussain
- Tue, 25 Mar 2025 06:11 PM (IST)
- Source:JND
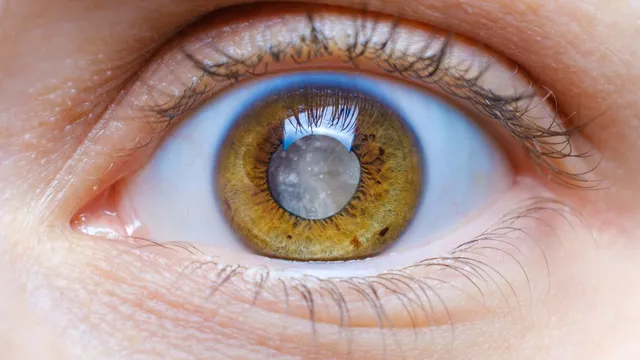
Cataracts, the clouding of the eye’s natural lens rank as one of the leading causes of blindness and vision impairment worldwide. While ageing and genetics have long been considered primary causes, recent research reveals that airborne pollutants are becoming major contributors to this rising trend. As air pollution levels surge, especially in urbanised and industrial areas, this public health issue is intensifying and may be driving a global uptick in cataract-related vision loss.
In a conversation with Jagran English, Dr. Ajay Sharma, Founder and Chief Medical Director of Eye-Q Eye Hospitals explained how airborne pollutants are increasing the risk of cataracts.
Environmental Pollutants And Eye Health
The growing body of research highlights the link between air pollution and eye health, particularly in the context of cataracts. Pollutants such as fine particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2) and ozone (O3) are known to contribute to the development of various eye diseases including cataracts. Fine particulate matter, in particular, is small enough to be inhaled deep into the lungs, from where it can enter the bloodstream, leading to widespread inflammation and oxidative stress. This systemic damage extends to the eyes where it accelerates oxidative damage to the lens, contributing to the formation of cataracts.
Lifestyle Factors And Regional Differences
Beyond environmental pollution, certain lifestyle and demographic factors contribute to the higher incidence of cataracts in specific populations. In India, for example, women aged 60 and above face a higher risk of cataracts due to prolonged exposure to biomass fuels used in cooking, a form of indoor air pollution. These pollutants much like outdoor air pollution, generate free radicals that damage the eye’s lens, leading to cataracts. In addition, smoking remains one of the most significant risk factors for cataract development.
E-Cigarettes: A New Concern
A growing area of concern in cataract research is the impact of e-cigarettes. Although promoted as a safer choice compared to traditional smoking, evidence indicates that e-cigarettes could pose comparable risks to eye health. The flavours in e-cigarettes have been shown to elevate free radical production, which accelerates oxidative damage to cellular DNA and plays a role in the development of cataracts. However, the long-term effects of e-cigarette use on cataract development are still under investigation.
Regional Variability In Cataract Prevalence
Cataract prevalence varies widely across regions, driven mainly by differences in air pollution levels, lifestyle habits and access to healthcare. In Southeast Asia, where air pollution levels are particularly high due to industrialisation and the widespread use of biomass fuels, cataract-related blindness is alarmingly prevalent, affecting up to 42% of the population.