- By Priyanka Munshi
- Wed, 27 Dec 2023 03:11 PM (IST)
- Source:JND
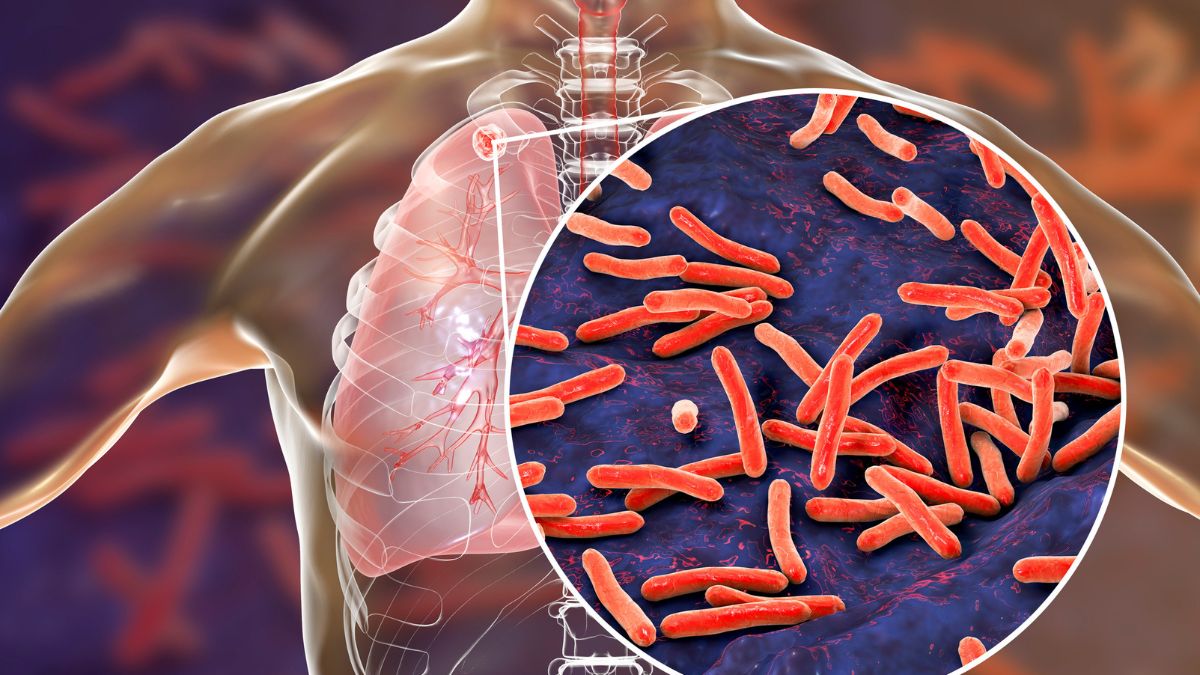
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the bacterial infection that causes tuberculosis, or TB. The primary tissue affected by this airborne disease is the lung, though it can also affect other organs. TB is extremely infectious because it spreads via the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. A persistent cough, unexpected weight loss, exhaustion, night sweats, and chest pain are some of the signs and symptoms of tuberculosis. Antibiotics can be used to treat tuberculosis (TB), but it's important to take the entire prescribed course in order to prevent drug-resistant strains.
People with weaker immune systems, such as those living with HIV, are also more susceptible to tuberculosis. Isolation and contact tracking are two public health methods that help stop the spread of an infectious disease, according to WebMD.
What Is Tuberculosis And How It Can Be Treated (Image Credit: Canva)
What Is The Cause Of Tuberculosis?
Similar to how the flu or cold spreads, tuberculosis bacteria do the same through the air. Individuals who have active tuberculosis cough, sneeze, talk, laugh, or sing, which might release inhaled droplets of germs. Although tuberculosis is not easily spread, if you spend more time indoors, you may easily contract it from friends, relatives, or coworkers.
Also Read:These 5 Spices Will Help You To Stay Naturally Warm In Winter Season
What Are The Types Of Tuberculosis?
Primary TB: The immune system can fail to completely eliminate the germs during the early stages of a tuberculosis infection, which leads to an absence of TB symptoms or flu-like symptoms.
Latent TB: All of the body's germs have the potential to become active even when they are not communicable. Medication may be necessary to prevent active tuberculosis in high-risk individuals, such as those with HIV, a history of infections, atypical chest X-rays, or compromised immune systems.
Active TB: Ninety percent of adult cases of TB are caused by latent infections, which occur when bacteria grow and spread the disease, making a person ill and possibly infecting others.
Active TB Outside The Lungs: Extrapulmonary tuberculosis, or active TB outside the lungs, is a tuberculosis infection that can have different symptoms depending on where it affects the body.

What Is Tuberculosis And How It Can Be Treated (Image Credit: Canva)
What Are The Symptoms Of Tuberculosis
- Feeling tired all the time
- Night sweats
- Chest pain
- Weight loss
- Coughing up blood
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- A cough that lasts more than 3 weeks
- Chills
Treatment Of Tuberculosis
Patients with latent tuberculosis are treated for at least three months with antibiotics that kill germs, such as isoniazid, rifampin, or rifapentine. If active tuberculosis is found, then you must visit the doctor right away.
Also Read: Resolutions List 2024: Make These 7 Promises To Yourself For Good Health In The New Year
A combination of drugs, such as ethambutol, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and rifampin, is used to treat active tuberculosis. These drugs are usually taken for six to twelve months.
Patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis can need to take several drugs for up to 30 months, and they might also have more side effects.